Home | Literatures | SEA WATER DESALINATION
Literatures
SEA WATER DESALINATION
Reverse Osmosis membranes must be rinsed and chemically cleaned periodically, when stopped or when performances decrease by 10-15%.
- Post service rinse
- Chemical cleaning
- Troubleshooting guide
Seawater flows tangentially along the membrane, creating an salt concentration gradient along the membranes length, the last element having the most concentrated brine bulk.
When the RO is stopped or in stand-by, natural osmosis will happen between the permeate side and the concentrate side containing high salinity brine. This can damage the feed spacers by creating a vacuum in the permeate line, as water will naturally flow back to the concentrate side, driven by osmotic pressure.
To avoid this natural damaging osmosis to happen, seawater and brine are flushed off the membranes after service by permeate water taken from the permeate tank (before chlorination) and pushed in the membrane by a low pressure pump (i.e., feed pump, distribution pump or specific cleaning pump)
Membrane Chemical cleaning
Seawater flows tangentially along the membrane, creating a boundary layer on the membrane surface.
Membranes have to cleaned typically when:
- Normalized Permeate flow varies by 10-15%
- Normalized Feed pressure varies by 10-15%
- Normalized Permeate conductivity varies by 10-15%
- Pressure drop between feed and concentrate varies by 10-15%
Normalized values take into account temperature and salinity variations in feed water.
In order to ease chronicle cleaning, our systems can be equipped with cleaning In Place (CIP) station, readily connected to the membranes rack:
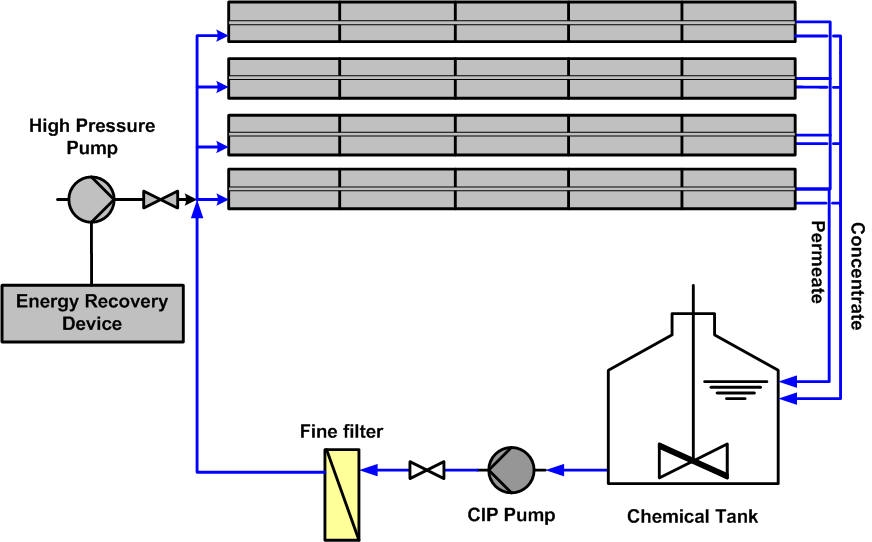
The CIP station, depending on the plant size includes a chemical tank with mechanical or manual stirrer, a CIP pump and a fine filter to avoid debris to enter the membranes. The chemical tank depends on the number of membranes to be cleaned at the same time.
Alkaline and Acid Cleaning solutions are recirculated around the membranes for at least 30 minutes.
We determine routine cleaning chemicals and procedures upon desalination plant layout and fouling identification:
RO Troubleshooting table: Analyzing the problem:
Permeate salinity
Permeate flow
Pressure drop
Possible cause
rapid increase
rapid decrease
rapid increase
Metal oxide fouling
marked increase
gradual decrease
gradual increase
Mineral scaling
slight increase
gradual decrease
gradual increase
Colloidal fouling
normal to increased
decreased
normal to increased
Polymerized silica
decreased
marked decrease
marked increased
Biological fouling
decreased
decreased
normal to increase
Organic fouling
increased
increased
increased
Chlorine damage
increased
increased
normal to decrease
Abrasion damages
increased
normal to increase
normal to decrease
O-ring leaks at inter-connectors or adapters
increased
normal to increase
normal to decrease
Glue line leaks due to permeate back pressure
Contact us for routine and specific cleaning
procedures
adapted to your system